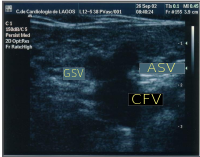
Mickey mouse signMickey Mouse signMickey Mouse sign is a medical sign resembling the head of Mickey Mouse, the Walt Disney character. Presented for the very first time at the CHIVA's Meeting, Berlin 2002 by Dr. Lurdes Cerol, this sign has been described as the image at the groin when a dilated accessory saphenous vein (ASV) exists: the common femoral vein (CFV) represents the head of Mickey Mouse while the great saphenous vein (GSV) and the dilated accessory saphenous vein (ASV) represent the ears. The presence of a Mickey Mouse sign has been a great diagnostic clue to check ASV insufficiency. Some authors, inspired by this sign, described an ecographic "Mickey Mouse View" at the saphenofemoral junction in the groin: the common femoral vein(CFV) represents the head of Mickey Mouse while the great saphenous vein (GSV) and the femoral artery (CFA) represent the ears.[1] But it can be seen in different regions of the body:
References[edit]
|
Clinicopathological findings and imaging features of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: comparison between contrast-enhanced ultrasound and contrast-enhanced computed tomographyAbstractPurposeIntraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct (IPNBs) are a group of rare lesions with uncertain clinical findings and imaging features. We aim to investigate the clinicopathological features and imaging findings of IPNBs on contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT). MethodsFrom February 2005 to March 2018, 30 patients with pathologically confirmed IPNBs were retrospectively identified in our hospital. Demographic, clinical, and pathological data, CEUS and CECT features and surgical strategies were analyzed. ResultsThe most common clinical manifestations were abdominal pain (53.3%), jaundice (23.3%), and acute cholangitis (10.0%). Among all lesions, 5/30 (16.7%) lesions presented as dilated bile ducts only, while 13/30 (43.3%) lesions presented as dilated bile ducts with intraductal papillary masses, and 12/30 (40.0%) presented as solid masses with dilated bile ducts. For the 20 patients who underwent both CEUS and CECT, 18 lesions were hyperenhanced on CEUS, and 17 lesions were hyperenhanced on CECT in the arterial phase. In total, 16 and 18 lesions showed washout in the portal and late phases on CEUS, while the corresponding number of lesions that showed washout in the portal and late phases on CECT were 11 and 13. Twelve lesions (40.0%) showed atypical hyperplasia, while 16/30 (53.3%) lesions underwent malignant transformations. ConclusionsThere are 3 major forms of IPNBs on grayscale ultrasound, including diffusely dilated bile ducts without visible mass; focal dilated bile duct with intraductal papillary masses; and solid mass surrounded by dilated bile ducts. The enhancement patterns of IPNBs on CEUS and on CECT were consistent. IPNB has a high malignant potential, and patients should be treated with surgical resection after the diagnosis is established. |
Adrenocortical hyperplasia: a review of clinical presentation and imagingAbstractAdrenal hyperplasia is non-malignant enlargement of the adrenal glands, which is often bilateral. It can be incidental or related to indolent disease process and may be related to benign or malignant etiologies causing biochemical alterations in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis which controls steroidogenesis and in particular cortisol production. Clinical significance of the adrenal hyperplasia is variable ranging from asymptomatic finding to serious manifestations of Cushing syndrome. This is often associated with anatomical changes in the adrenal glands, which typically manifests as diffuse and sometimes nodular enlargement of the adrenal glands radiologically. Approaching adrenal hyperplasia requires careful clinical and biochemical evaluation in correlation with imaging review to differentiate ACTH-dependent and ACTH-independent etiologies. CT is the primary modality of choice for adult adrenal imaging owing to reproducibility, temporal and spatial resolution and broader access, while MRI often serves a complimentary role. Ultrasound and MRI are most commonly used in pediatric cases to evaluate congenital adrenal hyperplasia. This article will discuss the clinical presentation and imaging features of different types and mimics of adrenal cortical hyperplasia. |
Evaluating the inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease using magnetic resonance diffusion kurtosis imagingAbstractObjectivesTo explore the feasibility of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) for evaluating inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease (CD). Materials and methodsIn all, 51 CD patients were included, who were performed with consecutive enteroscopy, MR and DKI (b values = 0–2000 mm2/s). The lesions of bowel segments were graded as inactive (0–2), mild (3–6), and moderate–severe group (> 6) based on simplified endoscopic activity score for Crohn's disease (SES-CD), The abilities of the parameters of DKI and DWI in grading different activity lesions were compared. ResultsOne hundred and twenty-seven bowel segments including inactive (15), mild (45) and moderate–severe (67) were analyzed. ADC (r = − 0.627, p < 0.001), Dapp (r = − 0.381, p < 0.001) and Kapp (r = 0.641, p < 0.001) were correlated with SES-CD. These parameters were significantly different among the three groups (all p < 0.001). ROC analysis found ADC had the highest accuracy (AUC = 0.884, p < 0.001) to differentiate inactive from active group with the threshold at 0.865 × 10−3 mm2/s, which was slightly higher than Kapp (AUC = 0.867, p < 0.001) with the threshold at 0.645, and was obviously higher than Dapp (AUC = 0.726, p = 0.005). Similarly, ADC also had the highest accuracy (AUC = 0.846, p < 0.001) to differentiate inactive–mild from moderate–severe group with the threshold at 0.825 × 10−3 mm2/s, and minimally higher than Kapp (AUC = 0.843, p < 0.001) with the threshold at 0.695, and obviously higher than Dapp (AUC = 0.690, p < 0.001). ConclusionDKI is feasible and comparable to conventional DWI for the evaluation of inflammatory activity in CD. |
Magnetic resonance imaging as a non-invasive method for the assessment of pancreatic fibrosis (MINIMAP): a comprehensive study design from the consortium for the study of chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, and pancreatic cancerAbstractCharacteristic features of chronic pancreatitis (CP) may be absent on standard imaging studies. Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) techniques such as T1 mapping, extracellular volume (ECV) fraction, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC), MR elastography (MRE), and T1-weighted signal intensity ratio (SIR) have shown promise for the diagnosis and grading severity of CP. However, radiologists still use the Cambridge classification which is based on traditional ductal imaging alone. There is an urgent need to develop new diagnostic criteria that incorporate both parenchymal and ductal features of CP seen by MRI/MRCP. Designed to fulfill this clinical need, we present the MINIMAP study, which was funded in September 2018 by the National Institutes of Health. This is a comprehensive quantitative MR imaging study which will be performed at multiple institutions in well-phenotyped CP patient cohorts. We hypothesize that quantitative MRI/MRCP features can serve as valuable non-invasive imaging biomarkers to detect and grade CP. We will evaluate the role of T1 relaxometry, ECV, T1-weighted gradient echo SIR, MRE, arteriovenous enhancement ratio, ADC, pancreas volume/atrophy, pancreatic fat fraction, ductal features, and pancreatic exocrine output following secretin stimulation in the assessment of CP. We will attempt to generate a multi-parametric pancreatic tissue fibrosis (PTF) scoring system. We anticipate that a quantitative scoring system may serve as a biomarker of pancreatic fibrosis; hence this imaging technique can be used in clinical practice as well as clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of agents which may slow the progression or reverse measures of CP. |
Microvascular invasion and grading in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with major and ancillary features according to LIRADSAbstractPurposeTo assess major and ancillary parameters that could be correlated with Microvascular Invasion (MIV) and with histologic grade of HCC. Materials and methodsIn this retrospective study, we assessed 62 patients (14 women–48 men; mean age, 63 years; range 38–80 years) that underwent hepatic resection for HCC. All patients were subject to Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT); 40 to Magnetic Resonance (MR) study. The radiologist assessed major and ancillary features according to LIRADS (v. 2018) and reported any radiological accessory findings if detected. ResultsNo major feature showed statistically significant differences and correlation with grading. Mean ADC value was correlated with grading and with MIV status. No major feature was correlated to MIV; progressive contrast enhancement and satellite nodules showed statistically different percentages with respect to the presence of MIV, so as at the monovariate correlation analysis, satellite nodules were correlated with the presence of MIV. At multivariate regression analysis, no factor proved to be strong predictors of grading while progressive contrast enhancement and satellite nodules were significantly associated with the MIV. ConclusionMean ADC value is correlated to HCC grading and MIV status. Progressive contrast enhancement and the presence of satellite nodules are correlated to MIV status. |
Microwave ablation assisted by three-dimensional visualization system as local therapy for relapsed hepatoblastoma: a small pilot studyAbstractPurposeWe aimed to explore the feasibility of microwave ablation (MWA) assisted by three-dimensional visualization system for relapsed HB in children. MethodsFrom August 2014 to February 2017, five patients with relapsed HB were enrolled. A total of 12 liver tumors were treated with MWA assisted by a three-dimensional visualization system. Follow-up data were obtained in all patients. The residual liver volume, local tumor progression, new intrahepatic tumors, survival outcome, and complications were analyzed. ResultsAll tumors were completely ablated in a single session. The mean ablation time per tumor was 9.7 ± 8.6 min, and the median ablation/liver volume ratio was 2.37%. No local tumor progression was observed during a follow-up period of 9–39 months. All patients were still alive at the end of the follow-up. The median progression-free survival time after ablation was 9 months, and the median survival time after ablation was 12 months. No other complications were observed except for fever. ConclusionsMWA assisted by three-dimensional visualization system appears to be a safe and feasible local treatment for recurrent HB in pediatric patients. |
| The "paper-thin wall" appearance in acute mesenteric ischemia |
Demystifying the mesenteric root lesionsAbstractObjectiveThe aim of this article is to describe the normal anatomy of the root of the small bowel mesentery (RSBM) as well as the multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) features of the various primary and secondary lesions that affect the RSBM. ResultsThe small bowel mesentery attaches the jejunum and ileum to the posterior abdominal wall, the line of attachment forming the RSBM. Several primary as well as secondary lesions involve the RSBM. The RSBM has anatomical contiguity with the mesocolon and other peritoneal ligaments, which forms a route for the spread of infection, neoplasms as well as several other abdominal pathologies. MDCT plays an important role in the evaluation of mesenteric root lesions. ConclusionFamiliarity with the lesions involving the RSBM and their characteristic appearances on MDCT is important in giving thoughtful differential diagnosis and guiding the treating physician in further management. |
| Correction to: Imaging features of immune-mediated genitourinary disease The original version of this article was published with a error in the initials of the first, fifth and sixth author name: Jonathon Weber, Frank Miller and Jeanne Horowitz. The correct author's initials should be Jonathon D. Weber, Frank H Miller, and Jeanne M Horowitz. It is now corrected with this correction. |
ENT-MD Alexandros G. Sfakianakis,Anapafseos 5 Agios Nikolaos 72100 Crete Greece,00306932607174,00302841026182,alsfakia@gmail.com
Blog Archive
- ► 2020 (479)
-
▼
2019
(2381)
-
▼
May
(401)
-
▼
May 15
(30)
- European Radiology
- Neuroscience
- Abdominal Radiology
- Neuroradiology
- Coloproctology
- Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics
- Conservation Genetics
- Gastroenterology
- Fertility Science and Research
- Pharmacology
- Tropical Pathology
- Hematology
- Health & Allied Sciences
- Studia Logica
- Medical Humanities
- Environmental Science and Bio/Technology
- Anaesthesia
- Neurology
- Medical Journal of Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth
- Oral Care and Research
- Environmental Radioactivity
- Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
- Psychiatry
- Forensic Dental Sciences
- Clinical Practice
- Otolaryngology
- Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery
- Plastic Surgery
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Otolaryngology
-
▼
May 15
(30)
-
▼
May
(401)
About Me
Labels
Search This Blog
Wednesday, May 15, 2019
Abdominal Radiology
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Blog Archive
- Sep 24 (11)
- Sep 23 (70)
- Sep 20 (22)
- Aug 27 (2)
- Aug 25 (1)
- Aug 24 (2)
- Aug 20 (1)
- Aug 19 (1)
- Aug 18 (2)
- Aug 17 (1)
- Aug 16 (1)
- Aug 13 (1)
- Aug 12 (1)
- Aug 11 (1)
- Aug 10 (2)
- Aug 07 (1)
- Aug 06 (1)
- Aug 05 (1)
- Aug 04 (1)
- Aug 03 (1)
- Aug 02 (1)
- Jul 30 (1)
- Jul 29 (1)
- Jul 28 (1)
- Jul 27 (1)
- Jul 26 (1)
- Jul 23 (1)
- Jul 22 (1)
- Jul 21 (1)
- Jul 20 (1)
- Jul 19 (1)
- Jul 16 (1)
- Jul 15 (1)
- Jul 14 (1)
- Jul 13 (1)
- Jul 12 (1)
- Jul 09 (1)
- Jul 08 (1)
- Jul 07 (1)
- Jul 06 (28)
- Jul 05 (1)
- Jul 02 (1)
- Jul 01 (1)
- Jun 30 (1)
- Jun 29 (2)
- Jun 25 (1)
- Jun 24 (41)
- Jun 23 (7)
- Jun 22 (1)
- Jun 21 (1)
- Jun 18 (1)
- Jun 17 (1)
- Jun 16 (18)
- Jun 15 (1)
- Jun 14 (1)
- Jun 11 (1)
- Jun 10 (1)
- Jun 09 (36)
- Jun 08 (1)
- Jun 04 (1)
- Jun 03 (1)
- Jun 02 (1)
- Jun 01 (1)
- May 31 (8)
- May 28 (1)
- May 27 (1)
- May 26 (1)
- May 25 (1)
- May 24 (1)
- May 21 (40)
- May 19 (1)
- May 18 (1)
- May 17 (1)
- May 14 (2)
- May 13 (1)
- May 12 (1)
- May 10 (1)
- May 07 (1)
- May 06 (3)
- May 05 (2)
- May 03 (1)
- Apr 30 (1)
- Apr 28 (1)
- Apr 27 (1)
- Apr 26 (1)
- Apr 24 (1)
- Apr 22 (2)
- Apr 20 (1)
- Apr 16 (1)
- Apr 15 (1)
- Apr 14 (1)
- Apr 13 (1)
- Apr 10 (1)
- Apr 09 (1)
- Apr 08 (1)
- Apr 06 (2)
- Apr 05 (1)
- Apr 03 (1)
- Apr 02 (2)
- Apr 01 (2)
- Mar 30 (1)
- Mar 29 (1)
- Mar 27 (1)
- Mar 26 (1)
- Mar 24 (1)
- Mar 23 (1)
- Mar 20 (1)
- Mar 19 (1)
- Mar 18 (1)
- Mar 17 (1)
- Mar 16 (1)
- Mar 13 (1)
- Mar 11 (2)
- Mar 10 (1)
- Mar 08 (1)
- Mar 05 (3)
- Mar 04 (2)
- Mar 03 (2)
- Feb 27 (1)
- Feb 26 (2)
- Feb 24 (3)
- Feb 21 (2)
- Feb 20 (1)
- Feb 19 (1)
- Feb 16 (2)
- Feb 13 (1)
- Feb 12 (2)
- Feb 10 (3)
- Feb 09 (1)
- Feb 07 (1)
- Feb 05 (2)
- Feb 04 (1)
- Feb 03 (1)
- Feb 02 (4)
- Jan 30 (2)
- Jan 28 (1)
- Jan 27 (3)
- Jan 26 (1)
- Jan 23 (3)
- Jan 22 (1)
- Jan 21 (3)
- Jan 20 (2)
- Jan 19 (1)
- Jan 16 (1)
- Jan 15 (7)
- Jan 14 (6)
- Jan 12 (1)
- Jan 09 (2)
- Jan 07 (2)
- Jan 06 (3)
- Jan 04 (1)
- Jan 03 (1)
- Jan 02 (2)
- Jan 01 (1)
- Dec 31 (1)
- Dec 30 (2)
- Dec 29 (2)
- Dec 28 (1)
- Dec 26 (1)
- Dec 20 (1)
- Dec 17 (2)
- Dec 16 (1)
- Dec 13 (1)
- Dec 12 (1)
- Dec 11 (1)
- Dec 10 (1)
- Dec 09 (1)
- Dec 04 (1)
- Dec 03 (1)
- Dec 01 (1)
- Nov 30 (1)
- Nov 29 (1)
- Nov 27 (3)
- Nov 26 (1)
- Nov 25 (1)
- Nov 24 (4)
- Nov 23 (1)
- Nov 22 (1)
- Nov 21 (1)
- Nov 19 (2)
- Nov 17 (2)
- Nov 16 (1)
- Nov 14 (1)
- Nov 13 (1)
- Nov 12 (1)
- Nov 11 (2)
- Nov 10 (1)
- Nov 09 (1)
- Nov 07 (1)
- Nov 06 (1)
- Nov 05 (2)
- Nov 04 (3)
- Nov 03 (2)
- Nov 02 (1)
- Nov 01 (1)
- Oct 31 (1)
- Oct 30 (1)
- Oct 29 (1)
- Oct 28 (1)
- Oct 27 (1)
- Oct 26 (1)
- Oct 24 (1)
- Oct 23 (1)
- Oct 22 (1)
- Oct 21 (2)
- Oct 20 (1)
- Oct 18 (1)
- Oct 17 (2)
- Oct 15 (2)
- Oct 13 (2)
- Oct 12 (1)
- Oct 10 (2)
- Oct 09 (3)
- Oct 08 (1)
- Oct 07 (2)
- Oct 06 (2)
- Oct 05 (1)
- Oct 04 (1)
- Oct 02 (3)
- Oct 01 (1)
- Sep 30 (4)
- Sep 29 (3)
- Sep 27 (1)
- Sep 26 (2)
- Sep 25 (2)
- Sep 24 (3)
- Sep 23 (4)
- Sep 19 (3)
- Sep 18 (1)
- Sep 17 (4)
- Sep 16 (1)
- Sep 15 (1)
- Sep 12 (1)
- Sep 11 (2)
- Sep 10 (4)
- Sep 09 (1)
- Sep 08 (2)
- Sep 05 (4)
- Sep 04 (1)
- Sep 03 (3)
- Sep 02 (5)
- Sep 01 (2)
- Aug 30 (2)
- Aug 29 (3)
- Aug 28 (2)
- Aug 27 (1)
- Aug 26 (2)
- Aug 23 (1)
- Aug 22 (1)
- Aug 21 (3)
- Aug 19 (2)
- Aug 18 (3)
- Aug 17 (1)
- Aug 16 (1)
- Aug 15 (1)
- Aug 13 (1)
- Aug 12 (3)
- Aug 11 (6)
- Aug 08 (6)
- Aug 07 (9)
- Aug 06 (5)
- Aug 05 (8)
- Aug 04 (1)
- Aug 01 (5)
- Jul 31 (6)
- Jul 30 (7)
- Jul 29 (6)
- Jul 28 (7)
- Jul 27 (1)
- Jul 26 (1)
- Jul 25 (4)
- Jul 24 (7)
- Jul 23 (10)
- Jul 22 (4)
- Jul 21 (10)
- Jul 20 (8)
- Jul 19 (2)
- Jul 18 (3)
- Jul 17 (5)
- Jul 16 (8)
- Jul 15 (19)
- Jul 14 (15)
- Jul 13 (8)
- Jul 11 (13)
- Jul 10 (26)
- Jul 09 (4)
- Jul 08 (26)
- Jul 07 (7)
- Jul 05 (33)
- Jul 04 (10)
- Jul 03 (24)
- Jul 02 (26)
- Jul 01 (26)
- Jun 30 (23)
- Jun 29 (24)
- Jun 28 (14)
- Jun 27 (19)
- Jun 26 (8)
- Jun 25 (78)
- Jun 24 (19)
- Jun 23 (17)
- Jun 22 (25)
- Jun 21 (12)
- Jun 20 (34)
- Jun 19 (4)
- Jun 18 (1)
- Jun 17 (17)
- Jun 16 (23)
- Jun 14 (2)
- Jun 13 (16)
- Jun 12 (27)
- Jun 11 (30)
- Jun 10 (39)
- Jun 09 (3)
- Jun 08 (15)
- Jun 07 (5)
- Jun 06 (14)
- Jun 05 (16)
- Jun 04 (21)
- Jun 03 (14)
- Jun 02 (33)
- May 31 (4)
- May 30 (23)
- May 29 (8)
- May 28 (23)
- May 27 (16)
- May 26 (22)
- May 25 (8)
- May 24 (12)
- May 23 (7)
- May 22 (1)
- May 21 (36)
- May 20 (4)
- May 19 (21)
- May 17 (24)
- May 16 (17)
- May 15 (30)
- May 14 (19)
- May 13 (6)
- May 12 (18)
- May 09 (6)
- May 08 (3)
- May 07 (27)
- May 06 (1)
- May 05 (9)
- May 03 (7)
- May 02 (15)
- May 01 (34)
- Apr 29 (34)
- Apr 27 (18)
- Apr 25 (19)
- Apr 24 (1)
- Apr 23 (9)
- Apr 22 (23)
- Apr 21 (14)
- Apr 19 (10)
- Apr 18 (34)
- Apr 17 (12)
- Apr 16 (19)
- Apr 15 (12)
- Apr 14 (18)
- Apr 12 (5)
- Apr 11 (17)
- Apr 10 (12)
- Apr 09 (20)
- Apr 08 (14)
- Apr 07 (21)
- Apr 05 (1)
- Apr 04 (26)
- Apr 03 (9)
- Apr 02 (20)
- Apr 01 (22)
- Mar 31 (16)
- Mar 29 (7)
- Mar 28 (29)
- Mar 27 (6)
- Mar 26 (20)
- Mar 25 (18)
- Mar 23 (26)
- Mar 22 (3)
- Mar 20 (18)
- Mar 19 (19)
- Mar 18 (5)
- Mar 17 (2)
- Mar 16 (5)
- Mar 15 (7)
- Mar 14 (27)
- Mar 13 (7)
- Mar 12 (15)
- Mar 11 (1)
- Mar 10 (1)
- Mar 08 (1)
- Mar 07 (6)
- Mar 06 (4)
- Mar 04 (6)
- Mar 02 (4)
- Mar 01 (7)
- Feb 27 (3)
- Feb 26 (6)
- Feb 25 (2)
- Feb 24 (4)
- Feb 22 (2)
- Feb 21 (6)
- Feb 20 (9)
- Feb 19 (4)
- Feb 18 (11)
- Feb 16 (1)
- Feb 13 (8)
- Feb 11 (17)
- Feb 10 (4)
- Feb 07 (7)
- Feb 06 (1)
- Feb 01 (5)
- Jan 26 (2)
- Jan 24 (7)
- Jan 23 (1)
- Jan 22 (2)
- Jan 21 (2)
- Jan 20 (1)
- Jan 17 (10)
- Jan 16 (1)
- Jan 15 (1)
- Jan 14 (7)
- Jan 13 (35)
- Jan 10 (29)
- Jan 08 (2)
- Jan 07 (8)
- Jan 06 (2)
- Jan 05 (1)
- Jan 04 (8)
- Jan 03 (13)
- Jan 02 (12)
- Jan 01 (4)
- Dec 31 (7)
- Dec 30 (4)
- Dec 29 (6)
- Dec 28 (25)
- Dec 27 (6)
- Dec 26 (10)
- Dec 25 (1)
- Dec 24 (1)
- Dec 22 (3)
- Dec 21 (55)
- Dec 20 (71)
- Dec 19 (59)
- Dec 18 (89)
- Dec 17 (19)
- Dec 16 (15)
- Dec 15 (42)
- Dec 14 (57)
- Dec 13 (33)
- Dec 12 (51)
- Dec 11 (30)
- Dec 10 (47)
- Dec 09 (11)
- Dec 08 (46)
- Dec 07 (35)
- Dec 06 (54)
- Dec 05 (34)
- Dec 04 (50)
- Dec 03 (11)
- Dec 02 (9)
- Dec 01 (34)
- Nov 30 (43)
- Nov 29 (46)
- Nov 28 (28)
- Nov 27 (47)
- Nov 26 (37)
- Nov 25 (7)
- Nov 24 (37)
- Nov 23 (38)
- Nov 22 (15)
- Nov 21 (34)
- Nov 20 (40)
- Nov 19 (66)
- Nov 18 (10)
- Nov 17 (32)
- Nov 16 (49)
- Nov 15 (51)
- Nov 14 (40)
- Nov 13 (38)
- Nov 12 (25)
- Nov 11 (22)
- Nov 10 (13)
- Nov 09 (30)
- Nov 08 (40)
- Nov 07 (19)
- Nov 06 (62)
- Nov 05 (45)
- Nov 04 (37)
- Nov 03 (49)
- Nov 02 (17)
- Nov 01 (26)
- Apr 10 (380)
- Jan 08 (404)
- Dec 13 (358)
- Dec 12 (24)
- Dec 07 (304)
- Dec 06 (59)
- Nov 20 (419)
- Oct 30 (423)
- Sep 25 (333)
- Sep 24 (57)
- Sep 13 (290)
- Sep 12 (48)
- Aug 17 (389)
- Jul 31 (340)
- Jul 25 (349)
- Jul 20 (1)
- Jul 19 (443)
Labels
Pages
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health IJERPH, Vol. 17, Pages 6976: Overcoming Barriers to Agriculture Green T...
-
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health IJERPH, Vol. 16, Pages 2236: Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Nursing...
-
from Allergy and Immunology via a.sfakia on Inoreader https://ift.tt/2DtisMK
-
Abstract Background ADAR1 is an enzymatic protein, which catalyzes a RNA‐editing reaction by converting Adenosine to Inosine and its exp...
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.